Acupuncture is an efficient alternative therapy for excessive or insufficient sweating.
We are pleased to welcome your visit at Naum Acupunture 646-926-0410
As the outside temperature rises and the hot summer months approach, we often worry about awkward scenarios with soaked clothes and the subsequent stench from perspiration.
What is sweat?
Sweat/perspiration is a normal body process that is essential to preserving our general health and wellbeing. In response to overheating, physical exertion, intoxication, stressful or anxious situations, and drug side effects, our body's thermoregulatory system causes sweating that supports our body's homeostasis as described in both Eastern and Western medicine.
Water makes up 99% of sweat, with minerals and electrolytes making up the remaining 1%. This complicated mixture is secreted by the body's innumerable sweat glands. However, it can be differ in composition based on each person's present state of health, dietary preferences, use of medications, and amount of physical activity.
Overdraining these compounds through excessive sweat can be harmful to your health when you are weak or ill, and vice versa.

Pros and Cons of Perspiration
Pros include:
1. Detoxifictions through the removal of pathogenic factors from the body
2. Balance and harmony through controlling the flow of Qi and addressing
imbalances
3. Boost the body's inherent defense system through helping to enhance
circulation, lymphatic flow, oxygenation, nutrition delivery, and overall body mechanisms
4. Stress reduction and relaxation
Cons include:
1. Dehydration brought on by excessive sweating
2. Hypersensitivity to exercise or discomfort brought on by profuse sweating or a high body temperature
3. Inconsistencies and cautions regarding perspiration brought on by particular illness or drugs
4. Unbalance brought on by various health issues
In Eastern Medicine
Since it is a means of removing pathogenic factors including toxins, excessive heat, damp, and stagnation, perspiration is throught to be crucial to maintaining the body in balance. Sweat is controlled by the Heart, which also regulates blood flow in the body. Since the Heart derives its blood from fluids, excessive sweating affects the blood' s volume and its smooth flow. When the blood volume is low, perspiration drops, and vice versa.
Sweat is also connected to the Lung and the Spleen when there is a lack of Qi. Weak Lung can prevent pores from actively closing by leaving them open, which can cause instant perspiration. Weak Spleen can cause the body to become stagnant with excessive dampness.
In Eastern traditional medicine therapies, the first thing is to determine whether sweating is localized or generalized, and whether it happens more frequently at night while you sleep or on its own spontaneously during the day.
Sweating especially on the hands and feet is associated with the function of the Spleen and Stomach, which are in charge of digestion, to overflow dampness to extremities. So as to reduce sweating on the hands and feet, and maintain strength, the digestive system must be strengthened.
Heavy perspiration under the arms is frequently a sign of heat caused by an underactive liver, gallbladder, or triple burner. In these cases, it is critical to tonify weak organs and evacuate extra heat.
Eyebrow sweating is an indication of heat in the body brought on by blood stasis or by stagnant damp-heat.
When the body loses moisture and heat climbs up to the head, the head sweats a lot. It is necessary to enhance Yin/moisture and reduce Yang/heat in order to improve this condtion.
If you occasionally perspire during the day, it is possible that your yang Qi is weak and your sweat glands aren't closing properly. In this case, acupuncture and/or Qi tonifying herbal medicines can be helpful. Furthermore, if you frequently perspire at night, especially as you sleep, this is a sign that your body's Yin Qi is weak and that you need a treatment to strengthen it.
In Western Medicine
Excessive perspiration is caused by faulty nerve signals that cause the eccrine sweat glands to produce too much of teh neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Topical and oral medicines are used in therapies to inhibit active overproduction of acetylcholine. Surgery, ion therapy, and botox injection are used in removing sweat glands that lead to over perspiration.
Sweat Odor and Lifestyle
Lifestyle changes can have a major impact on sweating episodes including maintaining a balanced diet, controlling stress levels, maintaining good hygiene, dressing in breathable clothing made of natural fibers, etc. Embracing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress that is frequently associate with over-perspiration/Hyperhidrosis.
Prior to anything else, understanding the reasons why you sweat unnecessarily is essential to determine whether it benefits your health by expelling waste or whether it affects your frail body. You can see from the aforementioned examples that sweating has a close connection to heat and serves as a homeostatic mechanism.
When you need to sweat out heat from the body and improve Qi flow, you can eat foods that can facilitate sweating off heat from the body and enhancing Qi flow. Saunas and other active physical exercises can also be beneficial. On the other hand, you should avoid foods that make you sweat, such as spicy and salty foods, alcohol, strenuous activities and saunas if you want to minimize your heat consupmption wtihout perspiring. In short, excessive sweating might make you feel weaker by depleting your body's supply of fluids, minerals and electrolytes.
Acupuncture and otherTreatments
Acupuncture treatments offer a non-invasive holistic approach to addressing sweating episodes. By targeting specific meridian and associated organs, acupuncture aims to regulate the flow of Qi and blood and restore harmony within the body, potentially reducing or increasing the frequency and intensity of sweating episodes.
Herbal medicine along with acupuncture treatments also holds potential in managing sweating episodes. Consulting with a qualified practitioner can serve you with valuable insights and personalized treatment options for seeking suitable alternatives.
In contrast, as the widespred use of antiperspirants and deodorants has become more common to manage sweating epidosdes and body odor, it is forecasted that the market for those products is anticipated to increse with a growth of 6.25% in the next 6 years from its value at $25.45 billion in 2022.
While these products can be effective in temporarily mananging sweating and masking odor, they do not address the underlying causes of excessive or micor-perspiration. Moreover, some antiperspirants contain aluminum compounds that block sweat glands, raising concerns about potential long-term health effects.
It is important to strike a balance between personal hygiene and the natural processes of the body, considering alternatives that align with out overall health and well-being. In the quest of balance, it is essential to honor our bodies and listen to their needs. By harmonizing the ancient wisdom of Eastern traditional medicine with modern approaches, we can navigate the complexities of sweating issues and discover personalized solutions that can support our overall health and well-being.
Acupressure Points for Over or Less Perspiration
You can manually apply acupressure to the following point locations at home by massaging or pressing them to aid with hyperhidrosis/over-perspiration or microhidrosis/lack of sweating. However, finding a licensed acupuncturist and giving some time for treatments is the right way to improve sweating episodes and have the desired effects.
Acupressure points to have more sweating
1. HT8 - Shao Fu - Lesser Mansion
Location: Make a fist and press the point where the tip of the little finger touches between the 4th and 5th metacarpal bones on the palm.
2. LI4 - He Gu - Joining Valley
Location: In the middle of the 2nd metacarpal bone on radial side between the 1st and 2nd metcarpal bones on the dorsum of the hand.
3. LI11 - Qi Chi - Pool at the Crook
Location: In the depression at the lateral end of the transverse cubital crease when the elbow is flexed.
4. KD3 - Tai Xi - Great canyon
Location: In the depression between the tip of the medial malleolus and Achilles tendon.
Acupressure Points to have less sweating
1. LU7 - Lie Que - Broken Sequence
Location: In the depression right under the tip of the index finger when the index fingers and thumbs of both hands are crossed.
2. LI4 - He Gu - Indicated above
3. SP6 - San Yin Jiao - Three Yin Intersection
Location: In depression close to the medial crest of the tibia, 3 cun superior to the prominence of the medial malleolus
4. HT7 - Shen Men - Spirit Gate
Location: In the depression at the proximal border of teh pisiform bone at the wrist joint.
5. KD7 - Fuliu - Returning Current
Location: Three fingers up from KD3 indicated above.
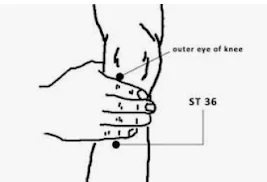
6. ST36 - Zusanli - Leg Three Miles
Location: Four fingers down below the outer eye of the knee.
Remember when applying pressure on each point, use steady and modate pressure, and hold each point for a few minutes while taking slow, deep breaths. It is advisable to consult with a qualified acupuncturist for personalized guidnce and to ensure proper use of acupressure points for your specific needs.
info@naumaculover.com










Comments
Post a Comment